Frequently Asked Questions About Debt Collection and Accounts Receivable Management
Debt collection companies specialize in accounts receivable management. Whenever commercial transactions take place, there is a debtor (the individual or entity that owes money) and a creditor (the individual or entity to whom money is owed). Collection agencies specialize in finding and negotiating with consumers and, in the event that the consumer refuses or is unable to pay, going through the legal process to ensure that a judgment is awarded and the creditor receives compensation from the consumer in so much as it is possible.
A “bonded” collection agency is one that has taken out a surety bond with an insurance company. Surety bonds are legally enforceable contracts between three parties: typically the principal (the collection agency), the obligee (the state government), and the surety (the insurance company that issues the bond). If the collection agency violates the terms of their bond (e.g. breaks a regulation or inappropriately handles payments), the state government can make a claim with the insurance company against the bond. The insurance company will evaluate the claim, pay it if it is determined to be valid, and then subsequently seek reimbursement from the collection agency.
29 out of 50 states require collection agencies to be bonded in order to conduct business.
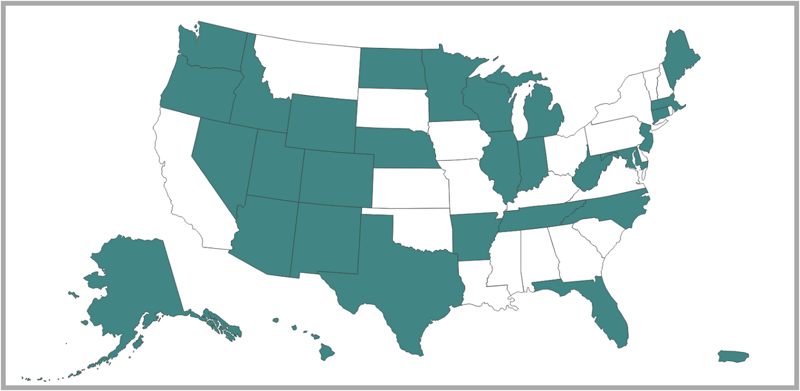
States And Territories That Require Collection Agencies To Be Bonded
Licensing requirements, bonding requirements, and the associated fees vary by state, which makes for a complicated landscape if you’re a collection agency trying to get started. Companies must comply with the requirements for the state(s) in which they practice. A list of the requirements by state can be found on the InsideARM website.
34 out of 50 states require collection agencies to be licensed in order to conduct business.
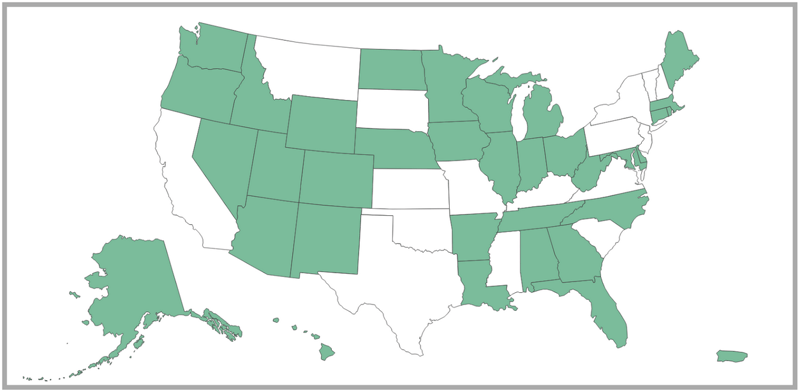
States And Territories That Require Collection Agencies To Be Licensed
Licensing requirements, bonding requirements, and the associated fees vary by state, which makes for a complicated landscape if you’re a collection agency trying to get started. Companies must comply with the requirements for the state(s) in which they practice. A list of the requirements by state can be found on the InsideARM website.
Skip tracing is a tool collection agency uses to locate the financial information, and contact information of a subject. A good collections agency has access to database information that allows them to locate debtors that have relocated without furnishing a forwarding address. Skip tracing is highly relevant if you’ve been attempting to contact the debtor and have been routinely ignored.
Subrogation is a synonym for “substitution.” In legal parlance it refers to the right of one party (typically an insurance company) to pay the obligation of a second party and then subsequently to collect from a third party (the debtor) after the fact.
